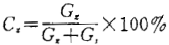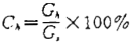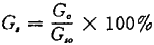1 Scope
This standard specifies the test methods for chemical properties of special industrial textiles (including cotton fiber, silk fiber and chemical fiber fabrics, ropes, belts and threads)
This standard is applicable to the test of special industrial textiles. Special industrial textiles with special requirements, if any, shall be specified in the quality standard of the product, or otherwise agreed by the supplier and the demander.
2 Reference standards
The following standards contain provisions that, through reference in this standard, constitute provisions of this standard. When the standard is published, the versions shown are valid. All standards will be revised. All parties using this standard should explore the possibility of using new versions of the following standards.
GB 8170-87 Rules for Rounding off Numerical Values
3 Sampling
3.1 Sampling for chemical property test shall be carried out in batches (or groups) according to different varieties, processing categories and use requirements.
3.2 Factory delivery test: one box (or roll, barrel, slot) of silk and cloth during processing is taken as a group, and one piece is sampled for each group; Take one sample per 100 kg for each group of strands processed according to different varieties; Ropes shall be grouped into three bundles and one sample shall be taken. For samples containing grease, pancreas and ash, one sample can be taken for each delivery batch.
3.3 The sample size shall be determined according to the test items and test methods.
3.4 The sample can be cut near the sampling place for physical and mechanical property test. In case of separate cutting, except for rope, belt and thread, cotton fabric shall be cut at least 2m away from the end of the piece, silk fabric and chemical fiber fabric shall be cut at least 4m away from the end of the piece, and in case of joint cutting, it can be cut at the joint opening of single piece.
3.5 The cut samples shall not be unevenly treated or poorly treated.
3.6 Each sample cut shall be labeled with the following items:
a) Product name;
b) Batch number (group number) and piece number (bundle number);
c) Sampling time.
3.7 The cut sample shall be wrapped with clean paper or fabric and sent to the laboratory to avoid impurities or acid-base substances that may affect the test results.
4 Test method for indicator reaction and pH pH determination
4.1 Test method of pH indicator reaction
4.1.1 Test instruments and appliances
a) 10ml graduated test tube or centrifuge tube (with test tube rack);
b) Nickel plated scissors;
c) 250 ml triangular flask;
d) 100 ml measuring cylinder.
4.1.2 Reagents
a) 0.05% methyl red solution;
b) 1% phenolphthalein solution.
4.1.3 Indicator preparation method
4.1.3.1 Preparation of 0.05% methyl red indicator: weigh 0.05 g of methyl red, dissolve it in 65 ml of reagent grade 95% alcohol, and add distilled water
35 ml of the solution was stirred well and left standing for several hours. Then, take the clear solution (discard the insoluble matter) and store it in a brown small mouth reagent bottle (re prepared after 6 months).
4.1.3.2 Preparation of 1% phenolphthalein indicator: weigh 1g of phenolphthalein and dissolve it in 100ml of reagent grade 95% alcohol, drop 0.1mol/L NaOH to a reddish color, and store it in a brown small mouth reagent bottle.
4.1.4 Operation steps
4.1.4.1 Method A (for silk fabrics)
1) Take 2g of sample, cut it into about 5cm ² with clean nickel plated scissors and put it into a 250ml triangular flask, then use a clean measuring cylinder to measure 100ml of distilled water and pour it into the triangular flask, move the triangular flask to an electrical or gas stove with asbestos mesh and heat it to a slight boiling point for 5-10 minutes, and design a method to cool it rapidly to room temperature.
2) Take two clean 10 ml graduated test tubes, first wash them three times with distilled water, then wash them twice with the above test solution, then inject 5ml of test solution into each test tube, drop a drop of phenolphthalein indicator into one tube, gently shake up and immediately observe the change of test solution in the tube. If the test solution should not be reddish, it is qualified (in terms of alkalinity), and drop two drops of methyl red indicator into the other tube, Shake it gently and observe the change of the test solution immediately. It is qualified if it is yellow (acidic), and use distilled water for blank test for comparison.
4.1.4.2 Method B (for cotton products)
Take a piece of cloth sample about 6 cm × 2 cm, cut it into pieces and put it into a test tube filled with 10 ml of distilled water, heat it to boil for 1 min, after cooling, divide the solution into two test tubes A and B, add 2-3 drops of 0.05% methyl red solution into tube A to measure the residual acidity on the fabric, and add one drop of 1% phenolphthalein indicator solution into tube B to measure the residual alkalinity on the fabric, Shake the test tube for several times. If the test solution in tube A is yellow and the test solution in tube B is colorless, it means that the pH is qualified. If the test solution in pipe A is red or the test solution in pipe B is rose red, it indicates that the pH is unqualified.
4.2 Test method for pH determination
4.2.1 Test instruments and appliances:
a) PH S-2 pH meter or the same type of pH meter;
b) 300 ml triangular flask; c) 200.ml measurement;
d) 100 ml beaker;
e) Reflux condenser;
f) Heating equipment.
4.2.2 Operation steps
Take several samples from different parts of the cloth sample, each about 2-3 g, cut and mix, weigh 5g of the mixed sample, put it into a 300 ml triangular flask, then put 100 ml of newly boiled neutral distilled water into the reflux condenser, boil it for 30 min, cool it to room temperature, pour the clear liquid into a dry and clean beaker, test it with a pH meter, and directly observe the pH reading, Just make a record.
4.3 Precautions
Distilled water must be tested with phenolphthalein indicator and methyl red indicator in advance. Similarly, it should be colorless when encountering phenolphthalein indicator and yellow when encountering methyl red indicator. If the methyl red indicator is red or orange when dropped into the distilled water, it may be caused by a large amount of carbon dioxide in the water. The distilled water should be poured into a clean glass container and boiled for more than 20 minutes, and then tested after cooling.
five Test method for slurries containing residual starch
5.1 Test tools: test tubes, heating equipment.
5.2 Test agent: 0.005 mol/L iodine solution.
5.3 Test operation: take about 6 × 2 cm cloth sample, cut it into pieces, put it into a test tube filled with 10 ml of neutral distilled water, heat and boil it for 1 min, add 1 ml 0.005 mol/L iodine solution after cooling, shake the test tube several times, and identify the desizing degree of the fabric according to the color of the test tube solution added with iodine solution. If the solution is blue or light blue, it is unqualified.
6 Test method for fat content and anti burning agent content
6.1 Test instruments and tools
a) Fat extractor (150 ml ball); b) Glass measurement (100 ml);
c) Water bath;
d) Silk bag (or cloth bag) without colloid;
e) Oven;
f) 1/10000 analytical balance.
6.2 Reagents
Organic solvent: petroleum ether (secondary reagent with boiling range of 60~90 ℃).
6.3 Test preparation
6.3.1 The fat extractor shall be washed with tap water, washed with distilled water, and then dried for standby.
6.3.2 The silk thin silk (or cotton thin cloth) without sericin shall be made into round simple silk (or cloth) bags, and the fat shall be removed with petroleum ether and absolute alcohol, and then stored in clean containers for standby. The size and height of round bags can be determined according to the size and height of the extractor in the fat extractor.
6.4 Operation steps
6.4.1 Take 4~5g of sample and put it into a clean white silk (or cloth) bag that has been cleaned of sericin, grease, pancreas and other impurities. Then put the silk bag containing the sample into the extractor in the middle part of a 150ml fat extractor, put a dried spherical bottle with known weight under it, and use a dry and clean measuring cylinder to measure about 120ml of reagent grade petroleum ether with a boiling range of 60~90 ℃, Pour it into the extractor, so that the petroleum ether flows into the spherical bottle through the siphon, insert the spherical condenser tube on it, connect the water inlet and outlet hose, and then put the whole set of fat extractor on the water bath for heating, so that the petroleum ether gas in the spherical bottle meets the condenser tube and becomes liquid drops, drop by drop on the sample, and allow the sample to have time to immerse the petroleum ether. That is to say, the sample must be placed under the bend of the siphon. When the petroleum ether drops to the bend of the siphon, the petroleum ether returns from the extractor to the spherical bottle due to the siphon effect, which is regarded as a primary reflux. Reflux for no less than 6 times (about 2 h), then take out the sample with bag, put it in clean glass or enamel ware to air dry, and use it for determination of pancreatic content after the petroleum ether is completely volatilized.
6.4.2 After the sample is taken out, still install the extractor and condenser tube overhead to recover the petroleum ether until there is no liquid drop in the condenser tube. Then remove the spherical bottle, put it on a boiling water bath for evaporation, remove the remaining petroleum ether, wipe the outside of the spherical bottle with a clean wiping cloth, move it into an 85~90 ℃ constant temperature oven for drying, place the spherical bottle in a dryer, cool it for more than 0.5h, weigh it accurately on a 1/10000 analytical balance, and then dry it in an 85~90 ℃ constant temperature oven, Then cool it in the dryer and weigh it accurately until it reaches constant weight.
6.5 Calculation method
The fat content and anti burning agent content are calculated according to the following formula:
G,=G-G G,= G.-G
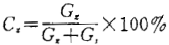
Where: G,—— Fat weight, g
G,—— Sample weight, g;
C. —— Fat content or anti burning agent content,%;
Gg - weight of empty spherical bottle, g
G ₉ - weight of empty spherical bottle, g;
Ga—— Weighing bottle weight plus sample weight, g;
G. -- Weight of empty weighing bottle, g。
7 Pancreatic content test method
7.1 Test instruments and appliances
Apparatus and tools for the same fat content test.
7.2 Reagents
Organic solvent: anhydrous ethanol (secondary reagent).
7.3 Test preparation
Preparation for test of the same fat content.
7.4 Operation steps
7.4.1 Put the dried sample (including bag) after extracting the fat from petroleum ether into a clean extractor, fill it with a spherical flask of known weight, pour 120 ml reagent grade absolute ethanol into the extractor with a clean and dry measurement, and then fill it with a condenser tube to heat it on the water bath, so that the condensate drops on the sample one by one, and the sample is not immersed in ethanol, Similarly, reflux shall not be less than 8 times (about 3-4 hours).
7.4.2 Remove the condenser tube, take out the sample (including the bag) and put it in a clean glass or enamel vessel, dry it through ventilation, then take out the sample from the silk (or cloth) bag, put it into a drying weighing bottle with known weight, dry it in a constant temperature oven at 85~90 ℃, move it into a dryer to cool it for more than 0.5 h, weigh it accurately on a 1/10000 analytical balance, and then dry it in an oven for 1 h after weighing, Then move into the dryer to cool for more than 0.5h, and weigh again until constant weight.
7.4.3 After the sample is taken out, still install the condenser tube to recover ethanol until there is no liquid drop in the condenser tube. Then remove the spherical bottle, evaporate it on a boiling water bath, remove the remaining ethanol, wipe the outside of the spherical bottle with clean wiping cloth, dry it in a constant temperature oven at 85~90 ℃, cool it in a dryer for more than 0.5 h, then accurately weigh it on a 1/10000 analytical balance, put it in an oven for drying for 1 h, and then cool it in a dryer for more than 0.5 h, Weigh again until constant weight.
7.5 Calculation method
The pancreatic content is calculated according to the following formula:
G,=G,y-G
G,=G.-G.

Where: G, —— g
G,- —— g
C,—— Pancreatic content,%;
Gy -- weight of empty spherical bottle plus pancreatic weight, g; G ₀ -- weight of empty spherical bottle, g:
Ga -- weight of weighing bottle plus weight of sample, g; G. -- Empty weighing bottle, g;
G,—— Fat weight, g。
8 Test method for ash content
8.1 Test instruments and appliances
a) Electric furnace (1000 ℃)
b) Magnetic crucible (40-50 ml);
c) Crucible clamp;
d) Nickel plated scissors.
8.2 Test preparation
Clean the unused new 40~50 ml magnetic crucible (with cover), dry it and put it into the electric melting furnace to gradually raise the temperature to 800 ℃, keep the constant temperature at 800 ℃, burn it for 2 hours, and then naturally cool it to about 100 ℃. Use the crucible pliers to move the burnt crucible into the dryer (at least 0.5h) for storage. If the old crucible continues to be used, it should be washed and dried first, then dried in an oven at 120 ℃ for 2-3 hours, and then moved into a dryer (at least 0.5 h) for storage.
8.3 Operation steps
Take about 2g of the sample, place it in a dry 40~50ml crucible of known weight, dry it for 2h in a 100~105 ℃ constant temperature oven, move it into a dryer to cool for more than 0.5h, then cover the crucible cover, accurately weigh it on a 1/10000 analytical balance, weigh it, put the crucible (remove the cover) into a 100~105 ℃ constant temperature oven to dry for 1h, and then cool it in a dryer for more than 0.5h, Then cover the crucible cover and weigh it accurately until the constant weight is reached. Then place it in an electric furnace for burning, and burn it at a constant temperature (800 ℃) until the sample turns into white ash (constant temperature time: about 3 h for silk fabric, about 1.5 h for viscose fabric sample, and about 2 h for viscose fabric sample). After the switch is turned off, the temperature will naturally drop to about 100 ℃. Use the crucible tongs to move the crucible into the dryer, cool it for more than 0.5 h, then cover the lid of the crucible, and quickly and accurately weigh it on the 1/10000 analytical balance.
8.4 Calculation method
The ash content is calculated according to the following formula:
G,=G,-G,
G=G, One G,
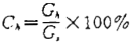
Where: G, Sample weight, g; G—— Ash weight, g CA -- ash content,%;
G. ——— Crucible weight plus sample weight, g; G, -- Crucible weight, g;
G ——— Crucible weight plus ash weight, g。
9 Test method for scouring degree
9.1 Test instruments and appliances a) 50 ml beaker;
b) Nickel plated scissors.
9.2 Reagent: carmine picric acid solution.
9.3 Reagent preparation method
Weigh 2g of reagent carmine, put it in a small beaker, add 10ml of chemically pure concentrated ammonia water and 20ml of distilled water, stir and heat with a glass rod to dissolve it, add 15ml of saturated picric acid solution, continue to stir, add distilled water to 100ml after cooling, and then adjust it to pH=9.5~10.5 with 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid.
9.4 Operation steps
Use clean nickel plated scissors to cut a sample of 4~5cm ², immerse it in carmine picric acid solution, take out the sample after 5min and wash it with clean water. If the color of the sample is lemon yellow, it is qualified; if it is orange or brownish red, it is unqualified.
10 Test method of iron content
10.1 Test instruments and tools
a) Magnetic evaporation vessel (8 cm);
b) Surface dish (9-10 cm);
c) Nickel plated scissors.
10.2 Reagents
a)1: 8 Dilute hydrochloric acid;
b) 10% ammonium thiocyanate.
10.3 Reagent preparation method
10.3.11:8 Dilute hydrochloric acid: measure 1 part of chemical pure or reagent grade concentrated hydrochloric acid with a specific gravity of 1.18~1.19, mix it with 8 parts of distilled water, and store it in a small mouth reagent bottle.
10.3.210% ammonium thiocyanate: weigh 10g of chemically pure ammonium thiocyanate and dissolve it in a small amount of distilled water, then add distilled water into 100ml, and store it in a small mouth reagent bottle.
10.4 Operation steps
Cut the sample with clean nickel plated scissors, the size of the sample is about 10 cm × 10 cm, put it in a clean and dry magnetic evaporating dish with appropriate diameter, and cover it with a surface dish with a larger diameter than the evaporating dish. When measuring, open the surface dish, add a few drops of 1:8 diluted hydrochloric acid, then add a few drops of 10% ammonium thiocyanate solution, and then cover it with a surface dish, Observe whether the sample shows red spots or stripes within 2 min.
11 Test method for impurity content of plant fiber
11.1 Test instruments and appliances
a) Beaker;
b) Tweezers;
c) Weighing bottle; d) Oven;
e) Dryer;
f) 1/10000 analytical balance. 11.2 Reagents
a) 10% NaOH solution;
b) Ethanol or ether.
11.3 Operation method
11.3.1 Sample 7~8g to measure its dry weight, and dissolve it in 400ml of 10% NaOH solution. After boiling for 15~20min, put the obtained solution on the copper wire mesh for filtration, and carefully clean the vegetable fiber impurities on the copper wire mesh with ethanol or ether until they are free of alkalinity (tested with phenolphthalein).
11.3.2 Remove the obtained plant fiber impurities from the filter with tweezers, put them into a pre weighed weighing bottle, and then put them into an oven with a temperature of 100~110 ℃ for drying for 3 hours. The dried residues are cooled in a dryer and weighed.
11.4 Calculation method
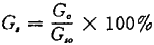
Where: G,—— Impurity content,% G.— — Weight of impurities, g G -- dry weight of sample, g。
12 Determination of copper content
12.1 Test instruments:
A) Automatic oven and tools:
B) Analytical balance;
C) High temperature furnace;
D) Measurement simplification;
E) Magnetic crucible;
F) 350 ml and 400 ml beakers;
G) watch glass;
H) Bottle washing;
I) Weighing bottle;
J) Buret;
k) Funnel
L) Filter paper;
m) Iodine volumetric flask.
12.2 Reagents
a) 6mol/L and 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid;
b) Ammonium chloride
c) 2% and 5% ammonia water;
d) 3mol/L sulfuric acid;
e) Glacial acetic acid;
f) Potassium iodide;
g) 0.5% starch solution;
h) Potassium hydrosulfide;
i) Sodium thiosulfate (0.02 mol/L).
12.3 Operation method
Take about 5g of sample and dry it to dry weight in a 100~105 ℃ drying oven. Weigh it on the analytical balance, record its weight, place the sample in a magnetic crucible, place it in a high temperature furnace, gradually raise the temperature to 700 ℃ and keep it for 2 hours to make the fabric burn into white ash (if the temperature in the high temperature furnace has risen, the sample is burned into ash on the electric furnace first, then moved to the high temperature furnace, and keep it for 2 hours at 700 ℃), After cooling, use 6 mol/L hot hydrochloric acid to dissolve about 25 ml in a 250 ml beaker, then use 1 mol/L hot hydrochloric acid to clean the burnt magnetic crucible until it is free of copper, and pour the washing solution into the beaker. Add 5g of ammonium chloride, heat and boil it, neutralize it with 2% ammonia water, continue to boil it until free chlorine disappears. At this time, the solution is blue-green. After cooling, filter the sediment and use about 50 ml of 0.5% ammonia water. Pour the filtrate of the washing solution into a 250 ml flask, continue to heat and boil it until ammonia disappears, neutralize it with 3 mol/L sulfuric acid until the blue-green just disappears (at this time, the solution is extremely pale yellow and colorless), Then drop ammonium hydroxide until the solution is light blue, then add 5 ml Bingkuai acid and 3g potassium iodide, place in a dark place for 8-10 min, and titrate with 0.02 mol/L sodium thiosulfate to light yellow, add 5 ml 0.5% starch solution as an indicator and a small amount of potassium hydrosulfide, and continue dropping until the blue disappears. Read the amount of sodium thiosulfate consumed.
13 Determination of free chlorine
13.1 Test instruments and appliances
a) Test tube rack and test tube
b) Test solution titration bottle
c) Table balance;
d) 50 ml measurement.
13.2 Reagents
a) 3 mol/L acetic acid:
b) 1% starch solution;
c) 1% potassium iodide solution (it must be noted that there is no free iodine).
13.3 Operation method
Take about 0.5g of sample (the fabric should be cut 10 cm from the edge of the cloth), cut it into pieces and put it into a clean test tube. Add 10 ml of distilled water, shake the test tube fully until the sample is completely wet, add 2-3 drops of 3 mol/L acetic acid, add 0.5 ml of 1% starch solution and 0.5 ml of 1% potassium iodide solution. If there is light violet blue on the sample, it means there is free chlorine.
14 Synthesis and retest of test results
14.1 For the sampling test results, if a certain index does not meet the standard, double number of samples shall be cut (one is at the connection of the original sample, and the other is cut at different positions) for the retest of the item. The retest results are qualified when both samples meet the standard.
14.2 If the manufacturer finds that the product still does not meet the standard after retest, in addition to the original sample of one piece as unqualified, the rest pieces can be sampled one by one for test. The test results shall be subject to one time, and retest is not allowed.
14.3 The calculation shall be calculated to four significant figures, and the rounding method for calculating the average shall be in accordance with the provisions of GB 8170.